# Input
## Table of Contents
1. [Gradle Dependency](#gradle-dependency)
2. [Text Input](#text-input)
1. [Basics](#basics)
2. [Hints and Prefill](#hints-and-prefill)
3. [Input Types](#input-types)
4. [Max Length](#max-length)
5. [Custom Validation](#custom-validation)
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/com/afollestad/material-dialogs/input)
The `input` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a text input dialog.
```gradle
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:input:3.3.0'
}
```
## Text Input
### Basics
You can setup an input dialog using the `input` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
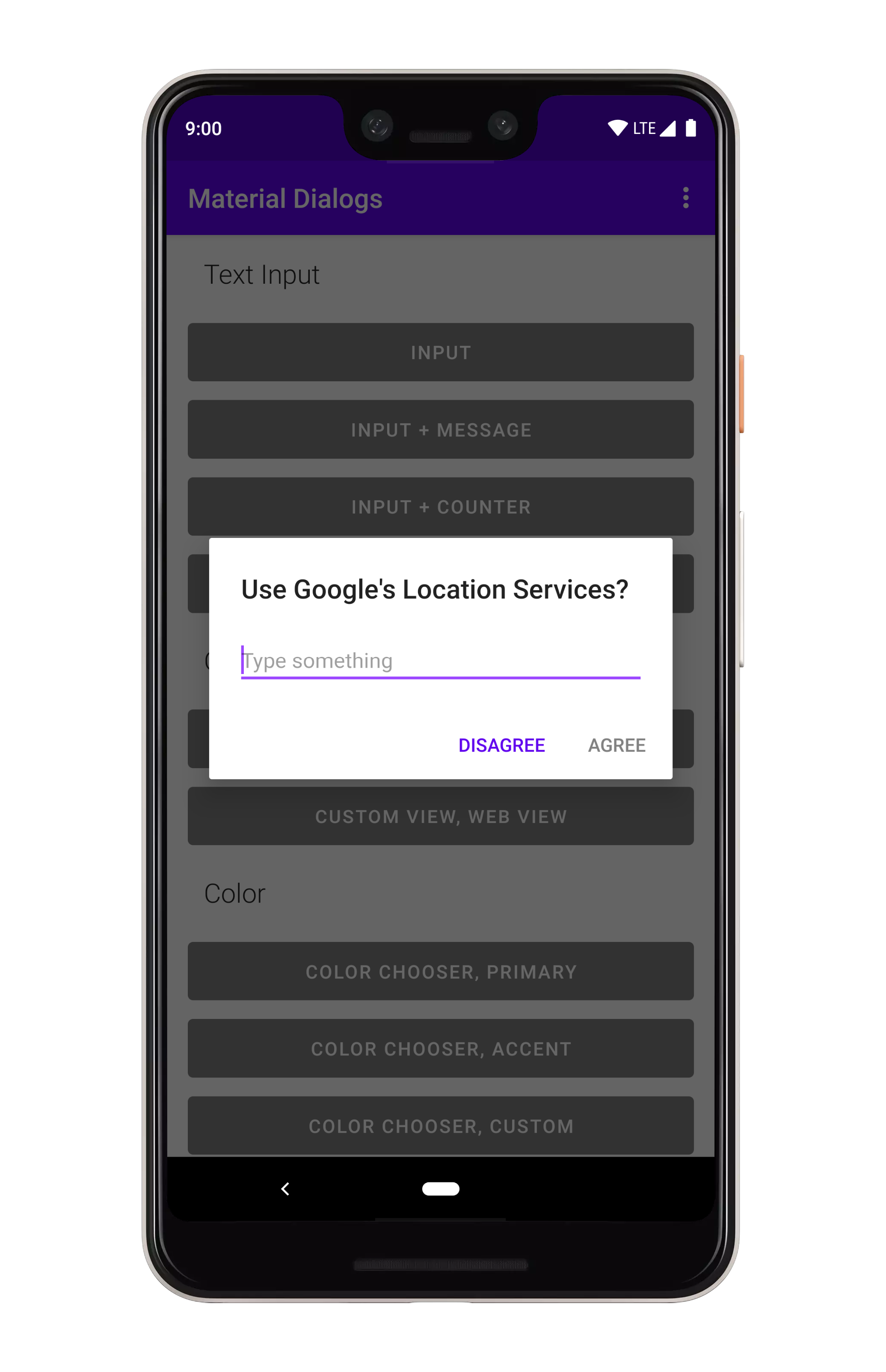 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input()
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
To allow the positive action button to be pressed even when the input is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(allowEmpty = true) { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button, might be an empty string`
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
}
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
}
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT or
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(inputType = type)
}
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input()
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
To allow the positive action button to be pressed even when the input is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(allowEmpty = true) { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button, might be an empty string`
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
}
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
}
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT or
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(inputType = type)
}
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
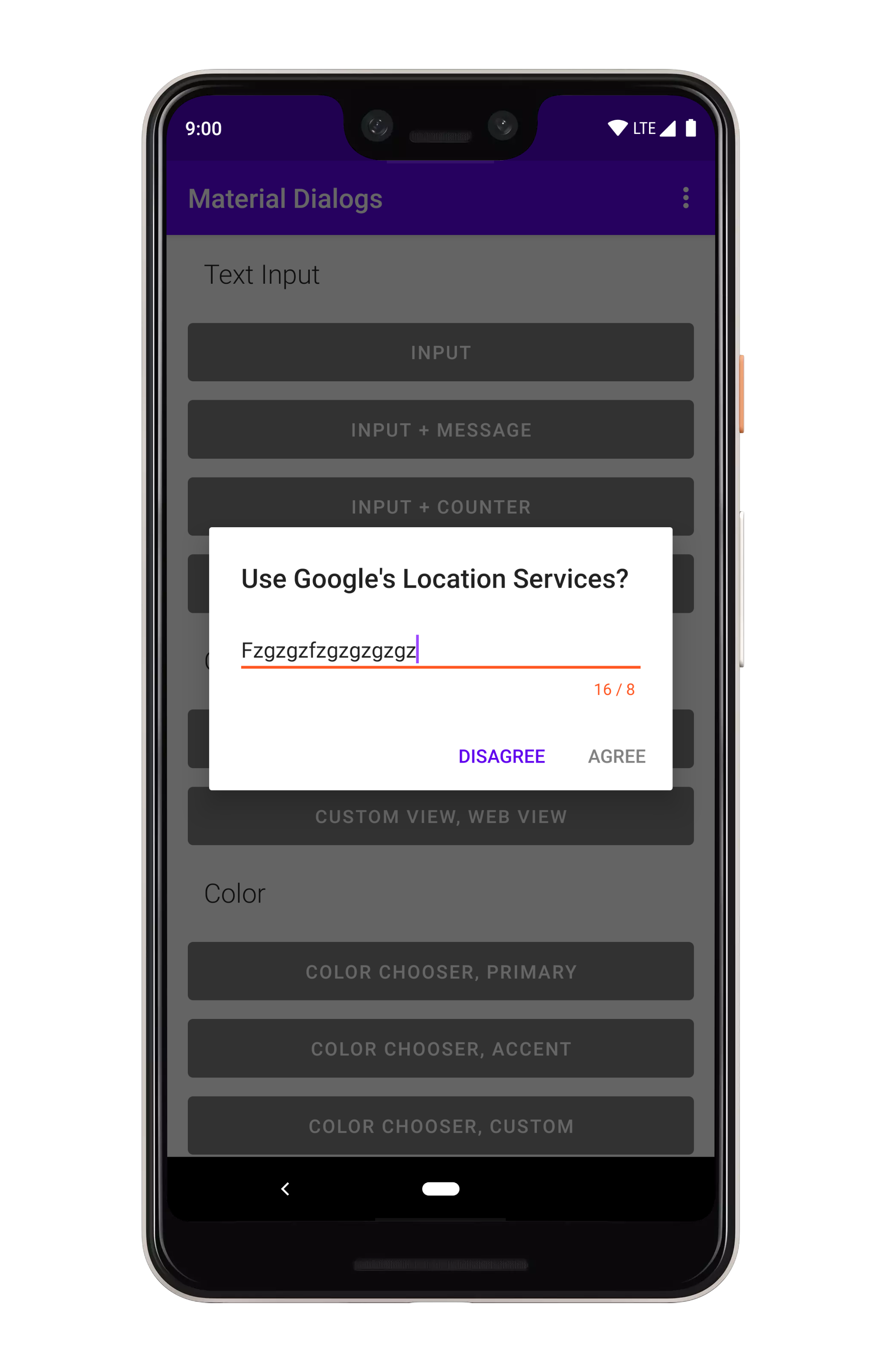 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(maxLength = 8)
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField?.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(maxLength = 8)
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField?.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input()
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
To allow the positive action button to be pressed even when the input is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(allowEmpty = true) { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button, might be an empty string`
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
}
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
}
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT or
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(inputType = type)
}
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input()
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
To allow the positive action button to be pressed even when the input is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(allowEmpty = true) { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button, might be an empty string`
}
positiveButton(R.string.done)
}
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
}
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
}
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
}
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT or
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(inputType = type)
}
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(maxLength = 8)
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField?.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(maxLength = 8)
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField?.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
positiveButton(R.string.submit)
}
```