# Material Dialogs
**Looking for the README for versions before 2.0? [Click here](README_OLD.md). Note that pre-2.0
versions will no longer receive support.**
[](https://travis-ci.org/afollestad/material-dialogs)
[](https://www.codacy.com/app/drummeraidan_50/material-dialogs?utm_source=github.com&utm_medium=referral&utm_content=afollestad/material-dialogs&utm_campaign=Badge_Grade)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
#### [View Releases and Changelogs](https://github.com/afollestad/material-dialogs/releases)

# Table of Contents - Core
1. [Gradle Dependency](#gradle-dependency)
2. [Changes in Version 2](#changes-in-version-2)
3. [Basics](#basics)
4. [Action Buttons](#action-buttons)
5. [Adding an Icon](#adding-an-icon)
6. [Callbacks](#callbacks)
7. [Kotlin Extras](#kotlin-extras)
8. [Dismissing](#dismissing)
9. [Lists](#lists)
1. [Plain](#plain)
2. [Single Choice](#single-choice)
3. [Multiple Choice](#multiple-choice)
4. [Custom Adapters](#custom-adapters)
10. [Checkbox Prompts](#checkbox-prompts)
11. [Custom Views](#custom-views)
12. [Miscellaneous](#miscellaneous)
# Table of Contents - Input
1. [Gradle Dependency](#gradle-dependency-1)
2. [Text Input](#text-input)
1. [Basics](#basics-1)
2. [Hints and Prefill](#hints-and-prefill)
3. [Input Types](#input-types)
4. [Max Length](#max-length)
5. [Custom Validation](#custom-validation)
# Table of Contents - Files
1. [Gradle Dependency](#gradle-dependency-2)
2. [File Choosers](#file-choosers)
1. [Basics](#basics-2)
2. [Filter](#filter)
3. [Empty Text](#empty-text)
3. [Folder Choosers](#folder-choosers)
1. [Basics](#basics-3)
2. [Filter](#filter-2)
3. [Empty Text](#empty-text-1)
# Table of Contents - Color
1. [Gradle Dependency](#gradle-dependency-3)
2. [Color Choosers](#color-choosers)
1. [Basics](#basics-4)
2. [Sub Colors](#sub-colors)
---
# Core
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Acore/_latestVersion)
The `core` module contains everything you need to get started with the library. It contains all
core and normal-use functionality.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:core:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Changes in Version 2
The whole library has been rebuilt, layouts and everything. The library is 100% Kotlin. APIs have
changed and a lot of things will be broken if you upgrade from the older version. Other things
to note:
1. **This library will be more opinionated. Not every feature request will be implemented.**
2. Minimum API level is 17 (Android Jellybean MR1).
3. There is no longer a separate `Builder` class, it's all-in-one.
4. The whole library was completely re-written in Kotlin. All the layouts and views were remade
as well. **This library is now designed specifically to work with Kotlin - it technically will
work with Java, but not pleasantly.**
5. All main classes exist in the `core` module, the extension modules take advantage of Kotlin
extensions to append functionality to it (such as input dialogs, color dialogs, etc.). This way,
you can include only what your app needs.
6. The use of the neutral button is deprecated to discourage use, see the
[newer Material guidelines](https://material.io/design/components/dialogs.html#actions).
7. *There is no longer a progress dialog included in library*, since they are discouraged by Google,
and discouraged by me. You should prefer a non-blocking inline progress indicator.
8. No dynamic color support, your dialogs will match your app theme. *I will be making sure
[Aesthetic](https://github.com/afollestad/aesthetic) works correctly with this library if you really
need dynamic theming.*
9. Other things will probably be added here.
## Basics
Here's a very basic example of creating and showing a dialog:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
.show()
```
`this` should be a `Context` which is attached to a window, like an `Activity`.
If you wanted to pass in literal strings instead of string resources:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(text = "Your Title")
.message(text = "Your Message")
.show()
```
Note that you can setup a dialog without immediately showing it, as well:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
dialog.show()
```
## Action Buttons
There are simple methods for adding action buttons:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
.show()
```
`this` should be a `Context` which is attached to a window, like an `Activity`.
If you wanted to pass in literal strings instead of string resources:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(text = "Your Title")
.message(text = "Your Message")
.show()
```
Note that you can setup a dialog without immediately showing it, as well:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
dialog.show()
```
## Action Buttons
There are simple methods for adding action buttons:
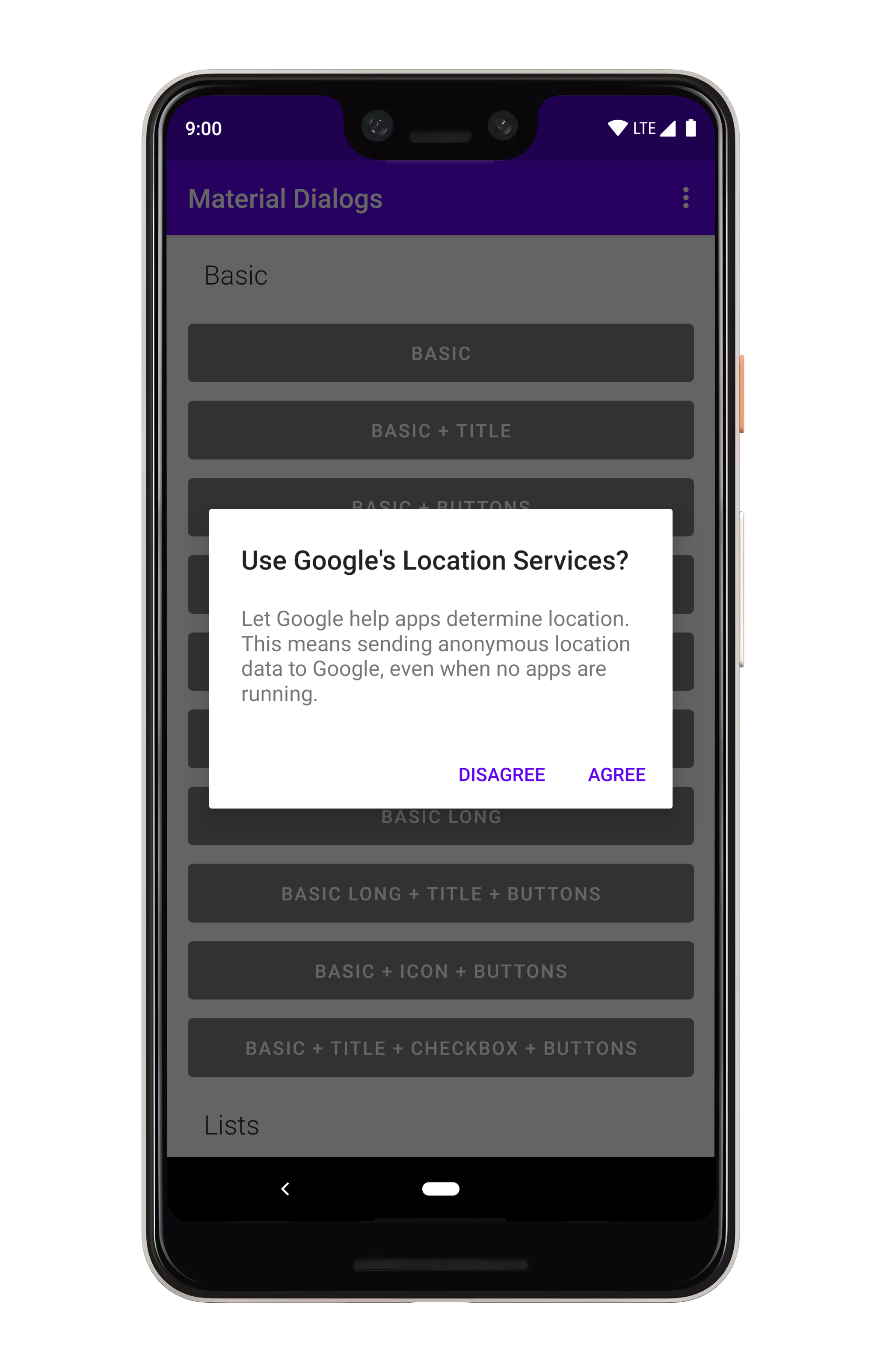 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree)
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree)
.show()
```
You can use literal strings here as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(text = "Agree")
.negativeButton(text = "Disagree")
.show()
```
---
Listening for clicks on the buttons is as simple as adding a lambda to the end:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.show()
```
If action buttons together are too long to fit in the dialog's width, they will be automatically
stacked:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree)
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree)
.show()
```
You can use literal strings here as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(text = "Agree")
.negativeButton(text = "Disagree")
.show()
```
---
Listening for clicks on the buttons is as simple as adding a lambda to the end:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.show()
```
If action buttons together are too long to fit in the dialog's width, they will be automatically
stacked:
 ## Adding an Icon
You can display an icon to the left of the title:
## Adding an Icon
You can display an icon to the left of the title:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.icon(R.drawable.your_icon)
.show()
```
You can pass a Drawable instance as well:
```kotlin
val myDrawable: Drawable = // ...
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.icon(drawable = myDrawable)
.show()
```
## Callbacks
There are a few lifecycle callbacks you can hook into:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.onPreShow { dialog -> }
.onShow { dialog -> }
.onDismiss { dialog -> }
.onCancel { dialog -> }
.show()
```
## Kotlin Extras
There's a cool way you can setup and show dialogs in a simple call with Kotlin:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
title(R.string.your_title)
message(R.string.your_message)
positiveButton(R.string.agree) { }
negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { }
}
```
## Dismissing
Dismissing a dialog closes it, it's just a simple method inherited from the parent `Dialog` class:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
dialog.dismiss()
```
## Lists
### Plain
You can show lists using the `listItems` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.icon(R.drawable.your_icon)
.show()
```
You can pass a Drawable instance as well:
```kotlin
val myDrawable: Drawable = // ...
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.icon(drawable = myDrawable)
.show()
```
## Callbacks
There are a few lifecycle callbacks you can hook into:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.onPreShow { dialog -> }
.onShow { dialog -> }
.onDismiss { dialog -> }
.onCancel { dialog -> }
.show()
```
## Kotlin Extras
There's a cool way you can setup and show dialogs in a simple call with Kotlin:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this).show {
title(R.string.your_title)
message(R.string.your_message)
positiveButton(R.string.agree) { }
negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { }
}
```
## Dismissing
Dismissing a dialog closes it, it's just a simple method inherited from the parent `Dialog` class:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
dialog.dismiss()
```
## Lists
### Plain
You can show lists using the `listItems` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
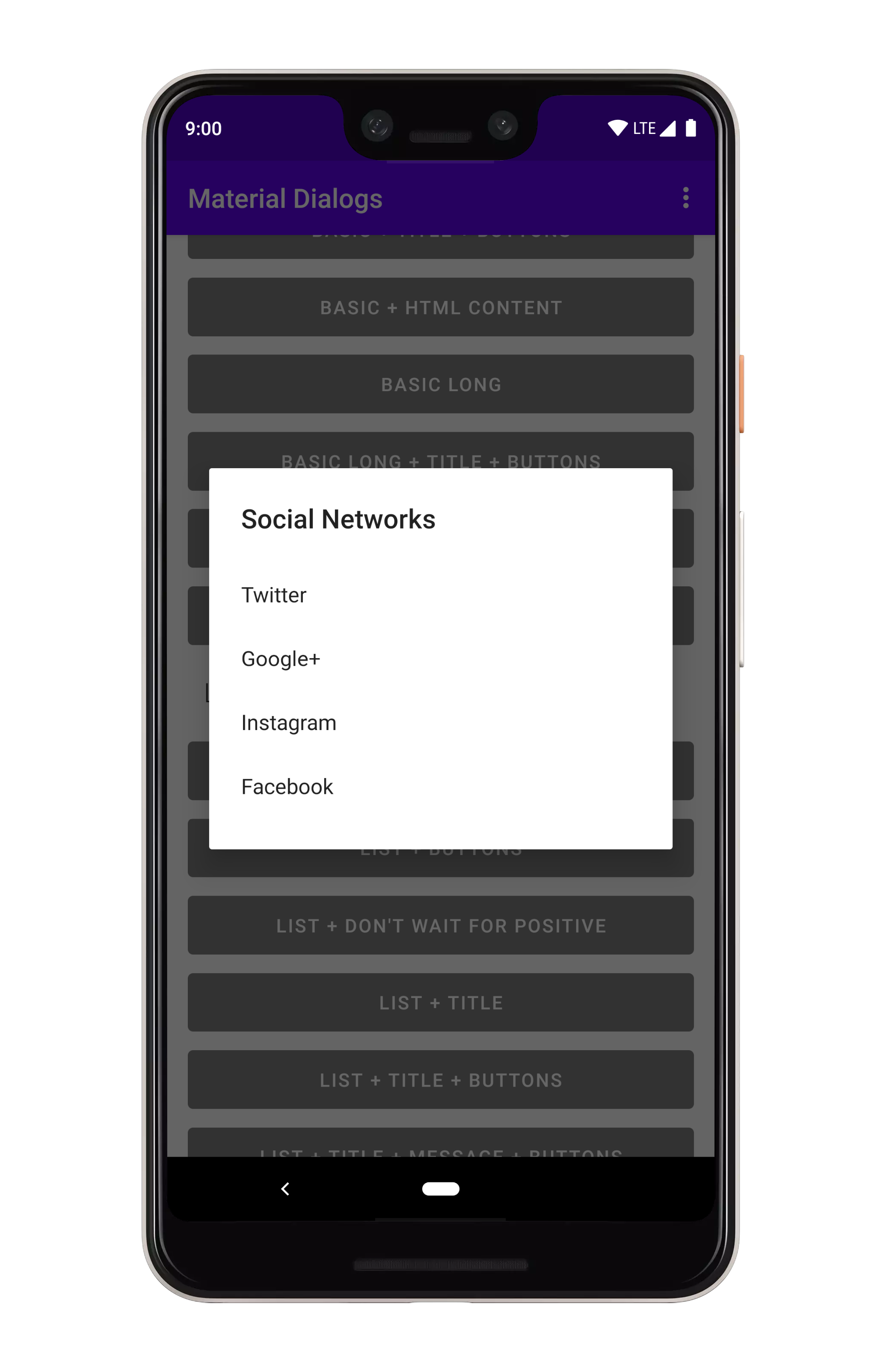 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks)
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(items = myItems)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user taps an item
}
.show()
```
### Single Choice
You can show single choice (radio button) lists using the `listItemsSingleChoice` extension
on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks)
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(items = myItems)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user taps an item
}
.show()
```
### Single Choice
You can show single choice (radio button) lists using the `listItemsSingleChoice` extension
on `MaterialDialog`:
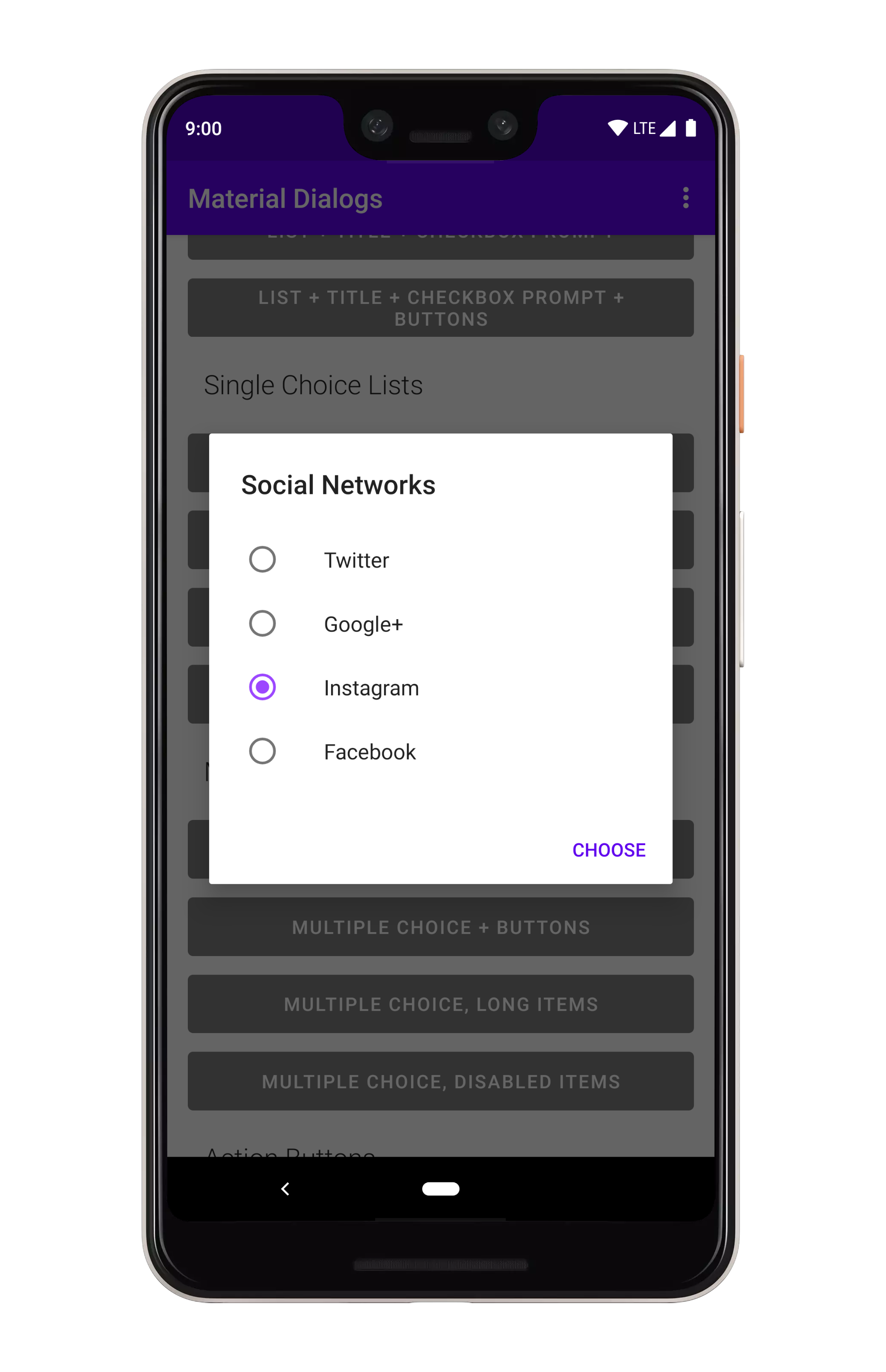 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want an option to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = 1)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user selects an item *and* taps the positive action
button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Multiple Choice
You can show multiple choice (checkbox) lists using the `listItemsMultiChoice` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want an option to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = 1)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user selects an item *and* taps the positive action
button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Multiple Choice
You can show multiple choice (checkbox) lists using the `listItemsMultiChoice` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
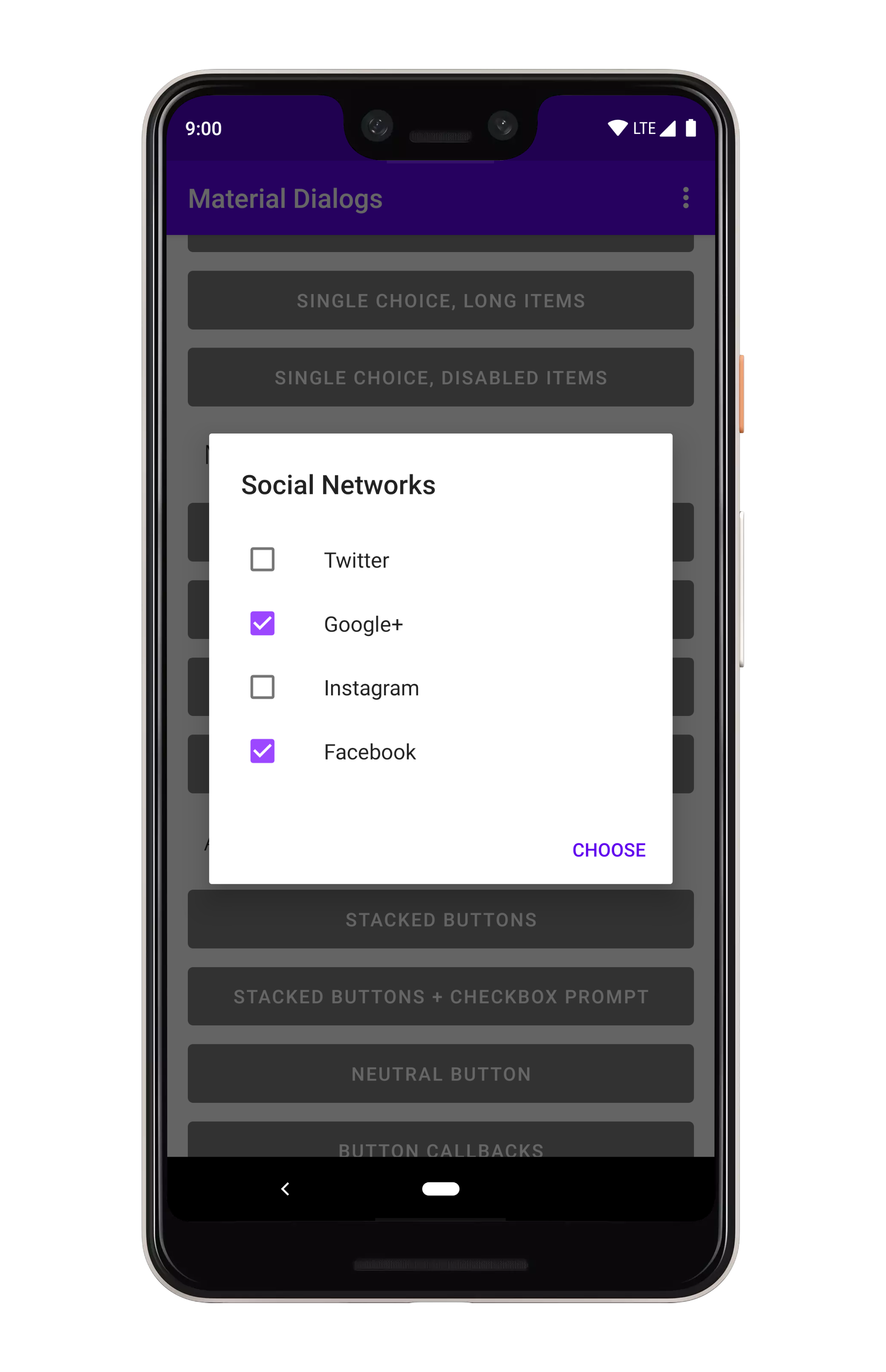 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want option(s) to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(1, 3)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = indices)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user select one or more items *and* taps the positive
action button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Custom Adapters
If you want to customize lists to use your own views, you need to use a custom adapter.
```kotlin
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = // some sort of adapter implementation...
MaterialDialog(this)
.customListAdapter(adapter)
.show()
```
You can retrieve your adapter again later from the dialog instance:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = dialog.getListAdapter()
```
You can also retrieve the `RecyclerView` that the adapter is hosted in:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val recyclerView: RecyclerView = dialog.getRecyclerView()
```
## Checkbox Prompts
Checkbox prompts can be used together with any other dialog type, it gets shown in the same view
which shows the action buttons.
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want option(s) to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(1, 3)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = indices)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user select one or more items *and* taps the positive
action button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Custom Adapters
If you want to customize lists to use your own views, you need to use a custom adapter.
```kotlin
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = // some sort of adapter implementation...
MaterialDialog(this)
.customListAdapter(adapter)
.show()
```
You can retrieve your adapter again later from the dialog instance:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = dialog.getListAdapter()
```
You can also retrieve the `RecyclerView` that the adapter is hosted in:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val recyclerView: RecyclerView = dialog.getRecyclerView()
```
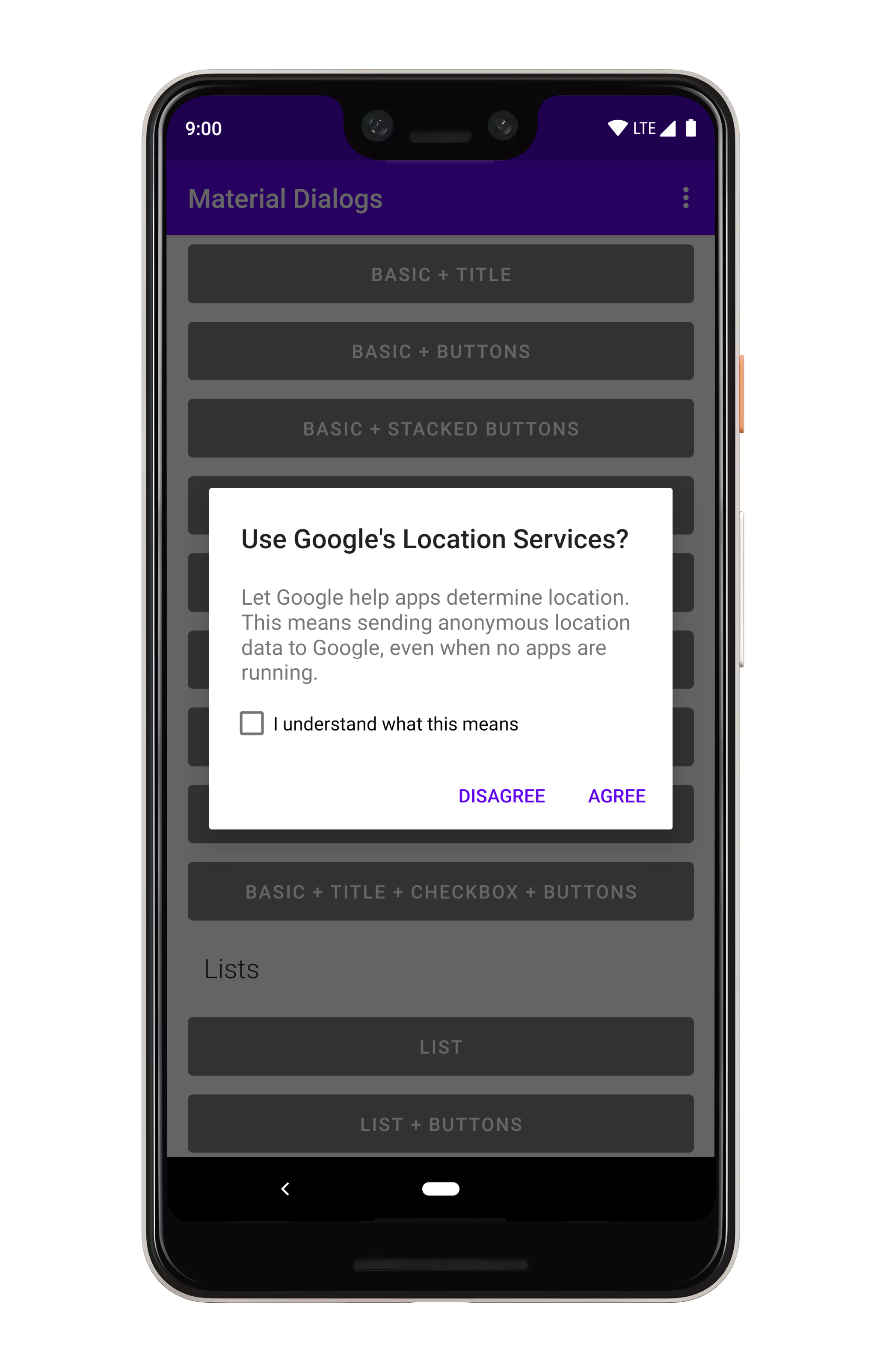
## Checkbox Prompts
Checkbox prompts can be used together with any other dialog type, it gets shown in the same view
which shows the action buttons.
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label) { checked ->
// Check box was checked or unchecked
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string for the label too:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World")
.show()
```
---
You can also append a lambda which gets invoked when the checkbox is checked or unchecked:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World") { checked -> }
.show()
```
If you only care about the checkbox state when the positive action button is pressed:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label)
.positiveButton(R.string.button_text) { dialog ->
val isChecked = dialog.isCheckPromptChecked()
// do something
}
.show()
```
## Custom Views
A lot of the included extensions use custom views, such as the color chooser dialog. There's also
a simple example in the sample project.
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label) { checked ->
// Check box was checked or unchecked
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string for the label too:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World")
.show()
```
---
You can also append a lambda which gets invoked when the checkbox is checked or unchecked:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World") { checked -> }
.show()
```
If you only care about the checkbox state when the positive action button is pressed:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label)
.positiveButton(R.string.button_text) { dialog ->
val isChecked = dialog.isCheckPromptChecked()
// do something
}
.show()
```
## Custom Views
A lot of the included extensions use custom views, such as the color chooser dialog. There's also
a simple example in the sample project.
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view)
.show()
```
You can also pass a literal view:
```kotlin
val myView: View = // ...
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(view = myView)
.show()
```
If your custom view may be taller than the dialog, you'll want to make it scrollable:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
.show()
```
For later access, you can use `dialog.getCustomView()`:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
val customView = dialog.getCustomView()
// Use the view instance, e.g. to set values or setup listeners
dialog.show()
```
## Miscellaneous
There are little details which are easy to miss. For an example, auto dismiss controls whether pressing
the action buttons or tapping a list item will automatically dismiss the dialog or not. By default,
it's turned on. You can disable it:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.noAutoDismiss()
.show()
```
---
# Input
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Ainput/_latestVersion)
The `input` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a text input dialog.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:input:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Text Input
### Basics
You can setup an input dialog using the `input` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view)
.show()
```
You can also pass a literal view:
```kotlin
val myView: View = // ...
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(view = myView)
.show()
```
If your custom view may be taller than the dialog, you'll want to make it scrollable:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
.show()
```
For later access, you can use `dialog.getCustomView()`:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
val customView = dialog.getCustomView()
// Use the view instance, e.g. to set values or setup listeners
dialog.show()
```
## Miscellaneous
There are little details which are easy to miss. For an example, auto dismiss controls whether pressing
the action buttons or tapping a list item will automatically dismiss the dialog or not. By default,
it's turned on. You can disable it:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.noAutoDismiss()
.show()
```
---
# Input
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Ainput/_latestVersion)
The `input` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a text input dialog.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:input:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Text Input
### Basics
You can setup an input dialog using the `input` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input()
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
.positiveButton(R.string.done)
.show()
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
.show()
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
.show()
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT and
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(inputType = type)
.show()
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input()
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
.positiveButton(R.string.done)
.show()
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
.show()
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
.show()
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT and
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(inputType = type)
.show()
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(maxLength = 8)
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()!!
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
---
# Files
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Afiles/_latestVersion)
The `files` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a file and folder chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:files:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
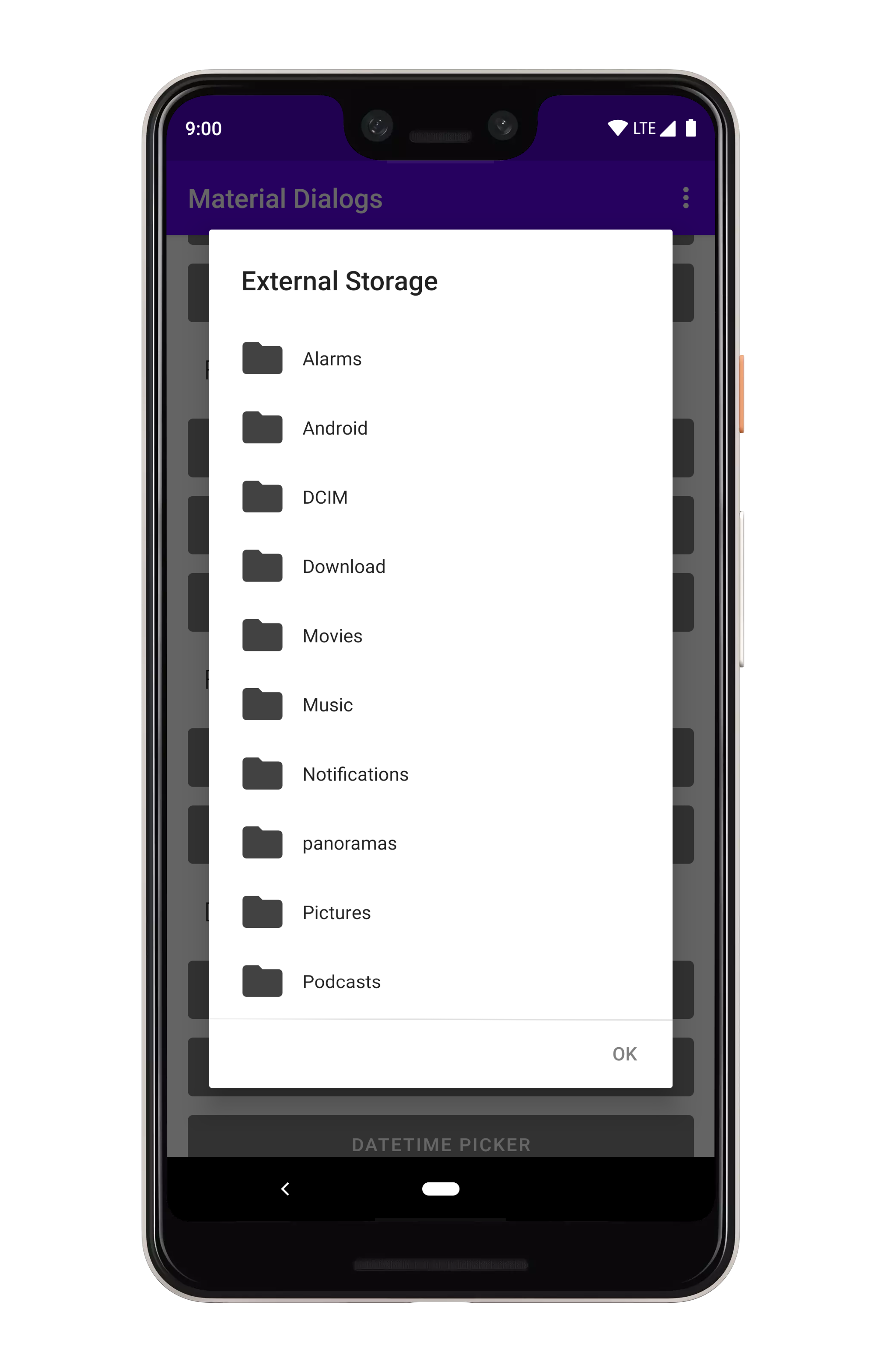
## File Choosers
### Basics
**Note:** File choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
You create file choosers using the `fileChooser` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(maxLength = 8)
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()!!
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
---
# Files
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Afiles/_latestVersion)
The `files` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a file and folder chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:files:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## File Choosers
### Basics
**Note:** File choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
You create file choosers using the `fileChooser` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
It shows all files and folders, starting in the external storage directory. Tapping a file invokes
the callback and dismisses the dialog.
You can change the directory which is listed initially:
```kotlin
val initialFolder = File(getExternalStorageDirectory(), "Download")
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(initialDirectory = initialFolder) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
**If a positive action button exists, tapping a file will select it, but the callback isn't invoked
until the positive action button is pressed.**
### Filter
A filter can be applied to only show the files and directories you wish to show:
```kotlin
// show ALL folders, and files that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.isDirectory || it.nameWithoutExtension.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
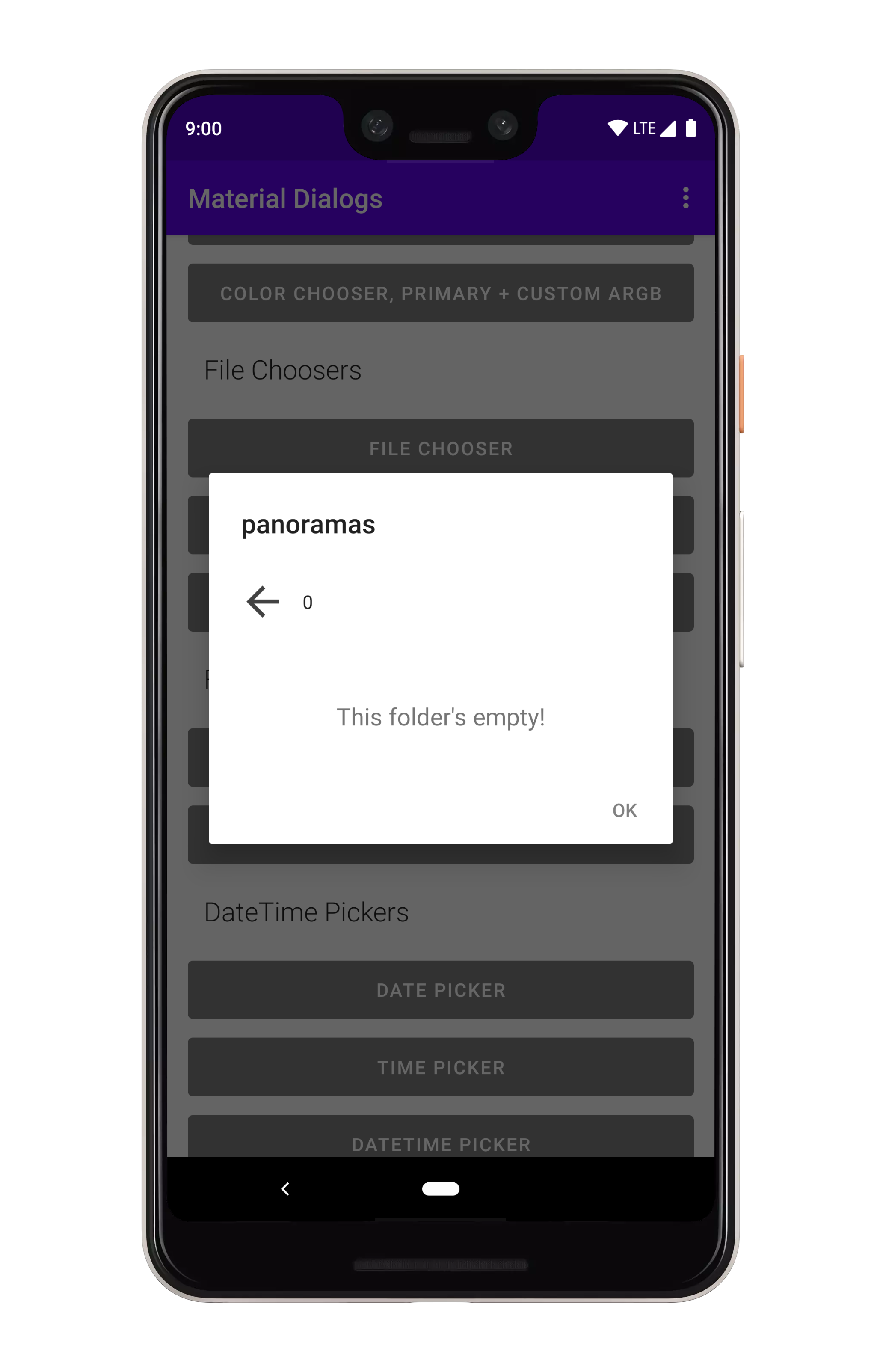
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
It shows all files and folders, starting in the external storage directory. Tapping a file invokes
the callback and dismisses the dialog.
You can change the directory which is listed initially:
```kotlin
val initialFolder = File(getExternalStorageDirectory(), "Download")
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(initialDirectory = initialFolder) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
**If a positive action button exists, tapping a file will select it, but the callback isn't invoked
until the positive action button is pressed.**
### Filter
A filter can be applied to only show the files and directories you wish to show:
```kotlin
// show ALL folders, and files that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.isDirectory || it.nameWithoutExtension.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
## Folder Choosers
**Note:** Folder choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
Folder choosers are basically the same as file choosers, with a few minor differences: 1) only folders
are shown, even when a custom filter is applied. 2) the selection callback is never invoked on a
item click, it only gets invoked with the currently viewed folder when the positive action button
is pressed.
### Basics
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser { dialog, folder ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Filter
You can apply a filter like you can with the file chooser.
```kotlin
// show only folders that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.name.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
---
# Color
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Acolor/_latestVersion)
The `color` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a color chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:color:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Color Choosers
### Basics
Color choosers show a simple grid of colors.
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
## Folder Choosers
**Note:** Folder choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
Folder choosers are basically the same as file choosers, with a few minor differences: 1) only folders
are shown, even when a custom filter is applied. 2) the selection callback is never invoked on a
item click, it only gets invoked with the currently viewed folder when the positive action button
is pressed.
### Basics
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser { dialog, folder ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Filter
You can apply a filter like you can with the file chooser.
```kotlin
// show only folders that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.name.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
---
# Color
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Acolor/_latestVersion)
The `color` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a color chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:color:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Color Choosers
### Basics
Color choosers show a simple grid of colors.
 ```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
You can specify an initial selection, which is just a color integer:
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, initialSelection = Color.BLUE) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
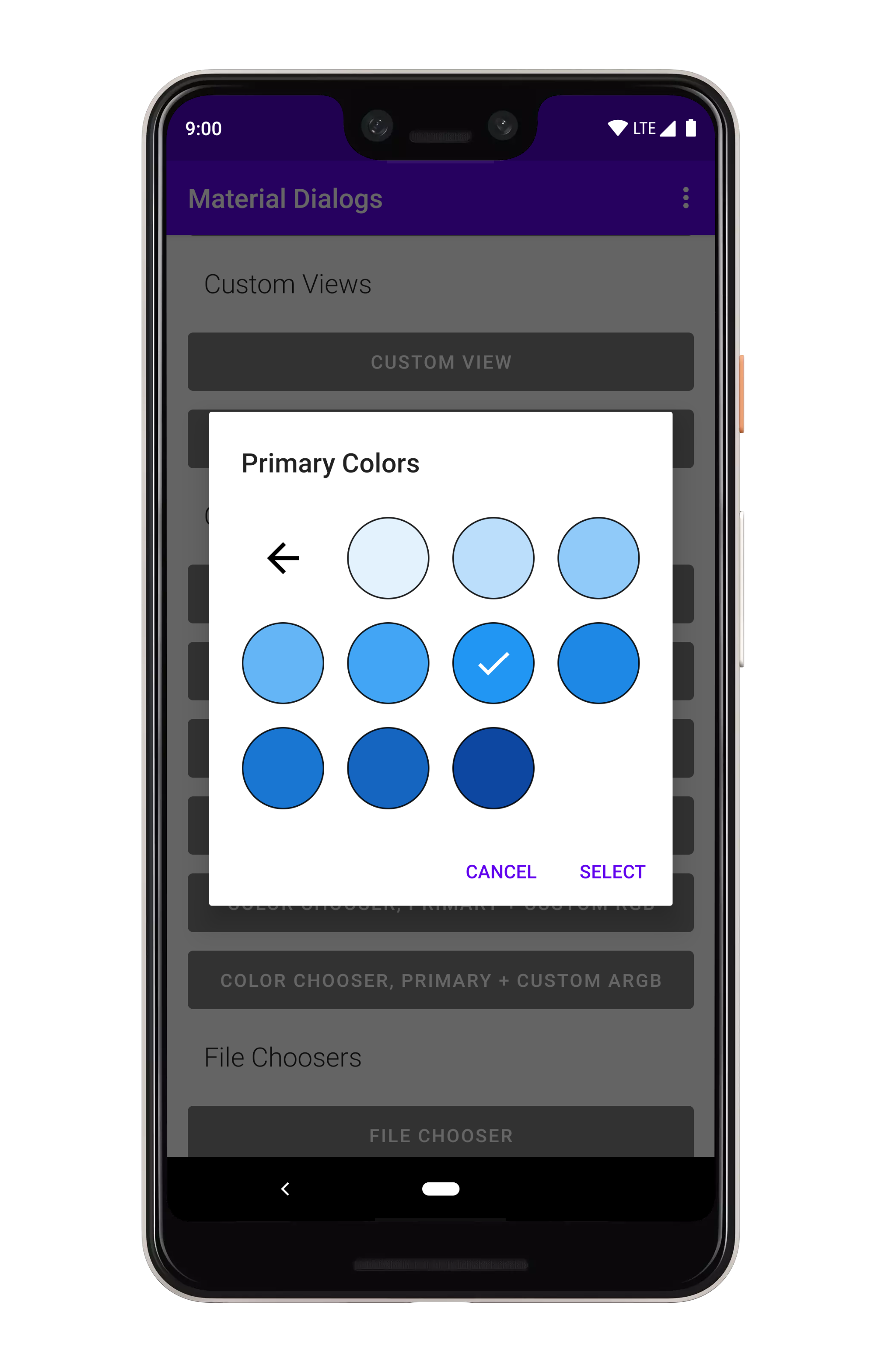
### Sub Colors
You can specify sub-colors, which are a level down from each top level color. The size of the top
level array must match the size of the sub-colors array.
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
You can specify an initial selection, which is just a color integer:
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, initialSelection = Color.BLUE) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
### Sub Colors
You can specify sub-colors, which are a level down from each top level color. The size of the top
level array must match the size of the sub-colors array.
 ```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE) // size = 3
val subColors = listOf( // size = 3
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_RED, Color.RED, Color.DARK_RED, Color.WHITE),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_GREEN, Color.GREEN, Color.DARK_GREEN, Color.GRAY),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_BLUE, Color.BLUE, Color.DARK_BLUE, Color.BLACK)
)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, subColors = subColors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE) // size = 3
val subColors = listOf( // size = 3
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_RED, Color.RED, Color.DARK_RED, Color.WHITE),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_GREEN, Color.GREEN, Color.DARK_GREEN, Color.GRAY),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_BLUE, Color.BLUE, Color.DARK_BLUE, Color.BLACK)
)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, subColors = subColors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
.show()
```
`this` should be a `Context` which is attached to a window, like an `Activity`.
If you wanted to pass in literal strings instead of string resources:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(text = "Your Title")
.message(text = "Your Message")
.show()
```
Note that you can setup a dialog without immediately showing it, as well:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
dialog.show()
```
## Action Buttons
There are simple methods for adding action buttons:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
.show()
```
`this` should be a `Context` which is attached to a window, like an `Activity`.
If you wanted to pass in literal strings instead of string resources:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(text = "Your Title")
.message(text = "Your Message")
.show()
```
Note that you can setup a dialog without immediately showing it, as well:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.your_title)
.message(R.string.your_message)
dialog.show()
```
## Action Buttons
There are simple methods for adding action buttons:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree)
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree)
.show()
```
You can use literal strings here as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(text = "Agree")
.negativeButton(text = "Disagree")
.show()
```
---
Listening for clicks on the buttons is as simple as adding a lambda to the end:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.show()
```
If action buttons together are too long to fit in the dialog's width, they will be automatically
stacked:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree)
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree)
.show()
```
You can use literal strings here as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(text = "Agree")
.negativeButton(text = "Disagree")
.show()
```
---
Listening for clicks on the buttons is as simple as adding a lambda to the end:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.positiveButton(R.string.agree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.negativeButton(R.string.disagree) { dialog ->
// Do something
}
.show()
```
If action buttons together are too long to fit in the dialog's width, they will be automatically
stacked:
 ## Adding an Icon
You can display an icon to the left of the title:
## Adding an Icon
You can display an icon to the left of the title:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks)
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(items = myItems)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user taps an item
}
.show()
```
### Single Choice
You can show single choice (radio button) lists using the `listItemsSingleChoice` extension
on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks)
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(items = myItems)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItems(R.array.socialNetworks) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user taps an item
}
.show()
```
### Single Choice
You can show single choice (radio button) lists using the `listItemsSingleChoice` extension
on `MaterialDialog`:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want an option to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = 1)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user selects an item *and* taps the positive action
button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Multiple Choice
You can show multiple choice (checkbox) lists using the `listItemsMultiChoice` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want an option to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = 1)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, index, text ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user selects an item *and* taps the positive action
button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsSingleChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Multiple Choice
You can show multiple choice (checkbox) lists using the `listItemsMultiChoice` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want option(s) to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(1, 3)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = indices)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user select one or more items *and* taps the positive
action button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Custom Adapters
If you want to customize lists to use your own views, you need to use a custom adapter.
```kotlin
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = // some sort of adapter implementation...
MaterialDialog(this)
.customListAdapter(adapter)
.show()
```
You can retrieve your adapter again later from the dialog instance:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = dialog.getListAdapter()
```
You can also retrieve the `RecyclerView` that the adapter is hosted in:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val recyclerView: RecyclerView = dialog.getRecyclerView()
```
## Checkbox Prompts
Checkbox prompts can be used together with any other dialog type, it gets shown in the same view
which shows the action buttons.
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { _, index, text ->
//
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string array too:
```kotlin
val myItems = listOf("Hello", "World")
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(items = myItems)
.show()
```
---
If you want option(s) to be selected when the dialog opens, you can pass an `initialSelection` index):
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(1, 3)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, initialSelection = indices)
.show()
```
To get item selection events, just append a lambda:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.show()
```
Without action buttons, the selection callback is invoked immediately when the user taps an item. If
you add a positive action button...
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items) { dialog, indices, items ->
// Invoked when the user selects an item
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
...then the callback isn't invoked until the user select one or more items *and* taps the positive
action button. You can override that behavior using the `waitForPositiveButton` argument.
An added bonus, you can disable items from being selected/unselected:
```kotlin
val indices = intArrayOf(0, 2)
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.listItemsMultiChoice(R.array.my_items, disabledIndices = indices)
.show()
```
### Custom Adapters
If you want to customize lists to use your own views, you need to use a custom adapter.
```kotlin
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = // some sort of adapter implementation...
MaterialDialog(this)
.customListAdapter(adapter)
.show()
```
You can retrieve your adapter again later from the dialog instance:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val adapter: RecyclerView.Adapter<*> = dialog.getListAdapter()
```
You can also retrieve the `RecyclerView` that the adapter is hosted in:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val recyclerView: RecyclerView = dialog.getRecyclerView()
```
## Checkbox Prompts
Checkbox prompts can be used together with any other dialog type, it gets shown in the same view
which shows the action buttons.
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label) { checked ->
// Check box was checked or unchecked
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string for the label too:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World")
.show()
```
---
You can also append a lambda which gets invoked when the checkbox is checked or unchecked:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World") { checked -> }
.show()
```
If you only care about the checkbox state when the positive action button is pressed:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label)
.positiveButton(R.string.button_text) { dialog ->
val isChecked = dialog.isCheckPromptChecked()
// do something
}
.show()
```
## Custom Views
A lot of the included extensions use custom views, such as the color chooser dialog. There's also
a simple example in the sample project.
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label) { checked ->
// Check box was checked or unchecked
}
.show()
```
You can pass a literal string for the label too:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World")
.show()
```
---
You can also append a lambda which gets invoked when the checkbox is checked or unchecked:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(text = "Hello, World") { checked -> }
.show()
```
If you only care about the checkbox state when the positive action button is pressed:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.checkBoxPrompt(R.string.your_label)
.positiveButton(R.string.button_text) { dialog ->
val isChecked = dialog.isCheckPromptChecked()
// do something
}
.show()
```
## Custom Views
A lot of the included extensions use custom views, such as the color chooser dialog. There's also
a simple example in the sample project.
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view)
.show()
```
You can also pass a literal view:
```kotlin
val myView: View = // ...
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(view = myView)
.show()
```
If your custom view may be taller than the dialog, you'll want to make it scrollable:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
.show()
```
For later access, you can use `dialog.getCustomView()`:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
val customView = dialog.getCustomView()
// Use the view instance, e.g. to set values or setup listeners
dialog.show()
```
## Miscellaneous
There are little details which are easy to miss. For an example, auto dismiss controls whether pressing
the action buttons or tapping a list item will automatically dismiss the dialog or not. By default,
it's turned on. You can disable it:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.noAutoDismiss()
.show()
```
---
# Input
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Ainput/_latestVersion)
The `input` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a text input dialog.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:input:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Text Input
### Basics
You can setup an input dialog using the `input` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view)
.show()
```
You can also pass a literal view:
```kotlin
val myView: View = // ...
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(view = myView)
.show()
```
If your custom view may be taller than the dialog, you'll want to make it scrollable:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
.show()
```
For later access, you can use `dialog.getCustomView()`:
```kotlin
val dialog = MaterialDialog(this)
...
.customView(R.layout.my_custom_view, scrollable = true)
val customView = dialog.getCustomView()
// Use the view instance, e.g. to set values or setup listeners
dialog.show()
```
## Miscellaneous
There are little details which are easy to miss. For an example, auto dismiss controls whether pressing
the action buttons or tapping a list item will automatically dismiss the dialog or not. By default,
it's turned on. You can disable it:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.noAutoDismiss()
.show()
```
---
# Input
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Ainput/_latestVersion)
The `input` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a text input dialog.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:input:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Text Input
### Basics
You can setup an input dialog using the `input` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input()
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
.positiveButton(R.string.done)
.show()
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
.show()
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
.show()
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT and
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(inputType = type)
.show()
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input()
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
With a setup input dialog, you can retrieve the input field:
```kotlin
val dialog: MaterialDialog = // ...
val inputField: EditText = dialog.getInputField()
```
---
You can append a lambda to receive a callback when the positive action button is pressed with
text entered:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input { dialog, text ->
// Text submitted with the action button
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
If you set `waitForPositiveButton` to false, the callback is invoked every time the text field is
modified:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
...
.input(waitForPositiveButton = false) { dialog, text ->
// Text changed
}
.positiveButton(R.string.done)
.show()
```
### Hints and Prefill
You can set a hint to the input field, which is the gray faded text shown when the field is empty:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hintRes = R.string.hint_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(hint = "Your Hint Text")
.show()
```
---
You can also prefill the input field:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefillRes = R.string.prefill_text)
.show()
```
A literal string can be used as well:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(prefill = "Prefilled text")
.show()
```
### Input Types
You can apply input types to the input field, which modifies the keyboard type when the field is
focused on. This is just taken right from the Android framework, the input type gets applied
directly to the underlying `EditText`:
```kotlin
val type = InputType.TYPE_CLASS_TEXT and
InputType.TYPE_TEXT_VARIATION_EMAIL_ADDRESS
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(inputType = type)
.show()
```
### Max Length
You can set a max length which makes a character counter visible, and disables the positive action
button if the input length goes over that:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(maxLength = 8)
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()!!
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
---
# Files
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Afiles/_latestVersion)
The `files` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a file and folder chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:files:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## File Choosers
### Basics
**Note:** File choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
You create file choosers using the `fileChooser` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input(maxLength = 8)
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
### Custom Validation
You can do custom validation using the input listener. This example enforces that the input
starts with the letter 'a':
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.input { dialog, text ->
val inputField = dialog.getInputField()!!
val isValid = text.startsWith("a", true)
inputField.error = if (isValid) null else "Must start with an 'a'!"
dialog.setActionButtonEnabled(POSITIVE, isValid)
}
.positiveButton(R.string.submit)
.show()
```
---
# Files
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Afiles/_latestVersion)
The `files` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a file and folder chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:files:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## File Choosers
### Basics
**Note:** File choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
You create file choosers using the `fileChooser` extension on `MaterialDialog`:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
It shows all files and folders, starting in the external storage directory. Tapping a file invokes
the callback and dismisses the dialog.
You can change the directory which is listed initially:
```kotlin
val initialFolder = File(getExternalStorageDirectory(), "Download")
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(initialDirectory = initialFolder) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
**If a positive action button exists, tapping a file will select it, but the callback isn't invoked
until the positive action button is pressed.**
### Filter
A filter can be applied to only show the files and directories you wish to show:
```kotlin
// show ALL folders, and files that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.isDirectory || it.nameWithoutExtension.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
It shows all files and folders, starting in the external storage directory. Tapping a file invokes
the callback and dismisses the dialog.
You can change the directory which is listed initially:
```kotlin
val initialFolder = File(getExternalStorageDirectory(), "Download")
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(initialDirectory = initialFolder) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
**If a positive action button exists, tapping a file will select it, but the callback isn't invoked
until the positive action button is pressed.**
### Filter
A filter can be applied to only show the files and directories you wish to show:
```kotlin
// show ALL folders, and files that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.isDirectory || it.nameWithoutExtension.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
 ```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
## Folder Choosers
**Note:** Folder choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
Folder choosers are basically the same as file choosers, with a few minor differences: 1) only folders
are shown, even when a custom filter is applied. 2) the selection callback is never invoked on a
item click, it only gets invoked with the currently viewed folder when the positive action button
is pressed.
### Basics
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser { dialog, folder ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Filter
You can apply a filter like you can with the file chooser.
```kotlin
// show only folders that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.name.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
---
# Color
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Acolor/_latestVersion)
The `color` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a color chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:color:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Color Choosers
### Basics
Color choosers show a simple grid of colors.
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
## Folder Choosers
**Note:** Folder choosers require your app to have permission to `READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE`, otherwise
directory listings will come back empty.
Folder choosers are basically the same as file choosers, with a few minor differences: 1) only folders
are shown, even when a custom filter is applied. 2) the selection callback is never invoked on a
item click, it only gets invoked with the currently viewed folder when the positive action button
is pressed.
### Basics
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser { dialog, folder ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Filter
You can apply a filter like you can with the file chooser.
```kotlin
// show only folders that start with the letter 'a'
val myFilter: FileFilter = { it.name.startsWith("a", true) }
MaterialDialog(this)
.folderChooser(filter = myFilter) { dialog, file ->
// Folder selected
}
.show()
```
### Empty Text
Empty text is shown when a folder has no contents. You can configure the empty text label:
```kotlin
MaterialDialog(this)
.fileChooser(emptyTextRes = R.string.custom_label) { dialog, file ->
// File selected
}
.show()
```
---
# Color
## Gradle Dependency
[  ](https://bintray.com/drummer-aidan/maven/material-dialogs%3Acolor/_latestVersion)
The `color` module contains extensions to the core module, such as a color chooser.
```gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.afollestad.material-dialogs:color:2.0.0-alpha03'
}
```
## Color Choosers
### Basics
Color choosers show a simple grid of colors.
 ```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
You can specify an initial selection, which is just a color integer:
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, initialSelection = Color.BLUE) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
### Sub Colors
You can specify sub-colors, which are a level down from each top level color. The size of the top
level array must match the size of the sub-colors array.
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
You can specify an initial selection, which is just a color integer:
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, initialSelection = Color.BLUE) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
### Sub Colors
You can specify sub-colors, which are a level down from each top level color. The size of the top
level array must match the size of the sub-colors array.
 ```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE) // size = 3
val subColors = listOf( // size = 3
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_RED, Color.RED, Color.DARK_RED, Color.WHITE),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_GREEN, Color.GREEN, Color.DARK_GREEN, Color.GRAY),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_BLUE, Color.BLUE, Color.DARK_BLUE, Color.BLACK)
)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, subColors = subColors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```
```kotlin
val colors = intArrayOf(Color.RED, Color.GREEN, Color.BLUE) // size = 3
val subColors = listOf( // size = 3
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_RED, Color.RED, Color.DARK_RED, Color.WHITE),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_GREEN, Color.GREEN, Color.DARK_GREEN, Color.GRAY),
intArrayOf(Color.LIGHT_BLUE, Color.BLUE, Color.DARK_BLUE, Color.BLACK)
)
MaterialDialog(this)
.title(R.string.colors)
.colorChooser(colors, subColors = subColors) { dialog, color ->
// Use color integer
}
.positiveButton(R.string.select)
.show()
```